Stock Market Game Lesson Plans Virginia SOL
The Stock Market Game is sponsored by the Virgina Council on Economic Education. As someone who has won district twice in Virginia for the Stock Market Game I wanted to share some resources I use with my students.
The Stock Market Game is reserved for my Senior Government classes. They do not have a state-test to take and it is easier to plan the time it takes to set-up and play. The Stock Market Game has a cost associated with it. For the past five years I have always found the money by applying for various grants particularly through Bayport Credit Union: Bayport Credit Union Grant.
To set-up the Stock Market Game I plan a curriculum that teaches students the basics of the game, how to read financial information, how to compare stocks, and how to search for stocks.
1. Stock Market Game Introduction Activities
The first activity is an outline of key vocabulary terms, what the stock market is etc. I also explain to students WHY we are doing this and how to win. I use a KWL Chart, notes, reading, and videos:
KWL Chart: Students create a 3-column sheet. The Topic is the Stock Market. Students fill in what they know and what they want to know about it. They will fill in the “L” column with what they learned about the Stock Market after the game is over.
SMG Introduction Notes : Introduction note sheet students fill in.
SMG Introduction Powerpoint: Introduction powerpoint in the Stock Market and the Stock Market Game.
Business and Investment in Market Economy Reading : Reading activity with questions for students to answer. I normally create a classroom set. We read it in class.
Stock Market Video(Youtube) and Stock Market Video Questions : I’ve tried finding various stock market videos that give a good generally outline of how it works. The best I have found is from the 1950s/1960s which, as reflective of the times, comes across as sexist and lacks diversity. I’ve included it but if someone knows of a better video please let me know.
2. Quiz:
After the introduction is complete I normally give the students a quiz over the information. Either I make the quiz-up or I use a quiz given by the Stock Market Game. Note: These quizzes may be out of date.
Stock Market Rules Quiz : Quiz over stock market and stock market game rules.
Stock Market Rules Quiz Answers : Answers of above quiz.
3. Stock Market Game Skills:
The next activities involve learning how to read stock information and how to search for it. I encourage students to use NYSE , NASADAQ ,or Google Finance to search for stock market information.
Jim’s Birthday Present Activity : I use this as a review of the above information. They brainstorm companies in bold. These will be used later on.
How to Interpret Stock Data from Internet: A handout with important stock terms. Students read the terms, discuss the terms and then fill in an example below using the stocks they brainstormed. Note: You may need to make modifications of this handout to reflect what is actually displayed on the stock page.
Stock Market Newspaper and Internet Analysis : A handout that walks students how to read financial information on a newspaper and on the internet. They should focus on the stocks they brainedstormed. Note: You may need to make modifications of this handout to reflect what is actually displayed on the stock page.
4. Stock Market Game Skill Practice:
When students are finished analyzing stocks. I give them their research sheets. Student’s will be divided into teams and will need to take on different roles. In these activities students are to practice their roles. They complete worksheets using the stocks the brainstormed. Depending on how much time you have you can assign all of them, combine them together, or assign a couple on each page. When students are done you could discuss which stocks they think will go up or down depending on their data.
Stock Market Game Roles : Description of team roles.
Technical Economic Research Coordinator : Quantitative Research Role (looking at numbers)
Basic Economic Research Coordinator : Qualitative Research Role (looking for news)
Sector Industry Worksheet : This worksheet can be done at the end of class or at the start of next class. It will introduce students to sector industries. Students can place their brainstormed stocks in the right sector and then conduct research and add additional stocks into the different sectors.
5a. Assigning Teams and Picking a Stock Market Game Name:
The final part before the game begins is to have students select their team name and assign roles of: Director, Technical, and Basic. If the group has 4 students I usually give another technical research sheet. I inform students that roles will rotate every two weeks.
Choosing a SMG Name Powerpoint: Powerpoint on creating a name
I normally assign students into teams of 3-4 individuals. Each class usually has about 8 teams. Each team gets a folder. Taped to the inside of the folder are their names and their team’s Stock Market Game password. Inside that folder is the following:
Stock Market Game Directions :An outline of the basic directions of the game. Note: these directions may have changed.
Director Record of Transactions: Director Role (completes a record of transactions of each day)
Technical Economic Research Coordinator : Quantitative Research Role (looking at numbers)
Basic Economic Research Coordinator : Qualitative Research Role (looking for news).
Note: If you are familiar with Google Docs you might be able to set-up/have students use Google Docs to enter their information.
5b. Create Name
To build their team they read over the Team Guidelines sheet and come-up with a name:
Team Building Guidelines : Guidelines for building a team.
5c. Logo Creation:
Once they have their name and I have approved it they create a logo and write their names on their folder.
5d: Consensus Chart
Upon completion of their name and logo I have each person in the group complete a consensus chart. Student’s grade each other using the following rubric.
4 person consensus chart : Rubric for students to grade each other.
6: Running the Stock Market Game and Grading
I usually run the stock market game in my class during school hours. I teach for about half the period and then let the students play the game. I try for having the students play the game at least twice a week. I do not get involved in what they are investing in. I let the students succeed or fail on their own. After all this is a learning activity. I aim to have students work on their stocks either on Monday or Friday of the week.
Grading: Their Stock Market Game grade is based on students grading themselves using the Consensus Sheet. I take an average of the grades. I also assign them an individual participation grade as well.
Sometimes I play Bloomberg Business while they are working. I also allow students to use their phones as students will download Stock Market Apps.
7. Other Activities
Warren Buffet Lesson Plan: A brief mini lesson plan on Warren Buffet. Student’s are introduced to Warren Buffet and why he is important. Student’s are encourage to try to invest in one of his companies OR a company he has invested in.
Investwrite: Students write an essay in response to an investment topic. These are competitive with awards and prizes given.
I also have students do research on a company they would like to work for. They present their findings to the class.
8. Advice
SMG Advice by Seniors : Some advice from my former students on playing the Stock Market Game.
9. Finishing up
At the end of the game, students complete the “Learn” part of their KWL chart. Student’s also write an essay (2-5 paragraphs) on what they learned. Alternatively, you could have them respond to the Invest Write essay without actually submitting it in.
10. Pictures
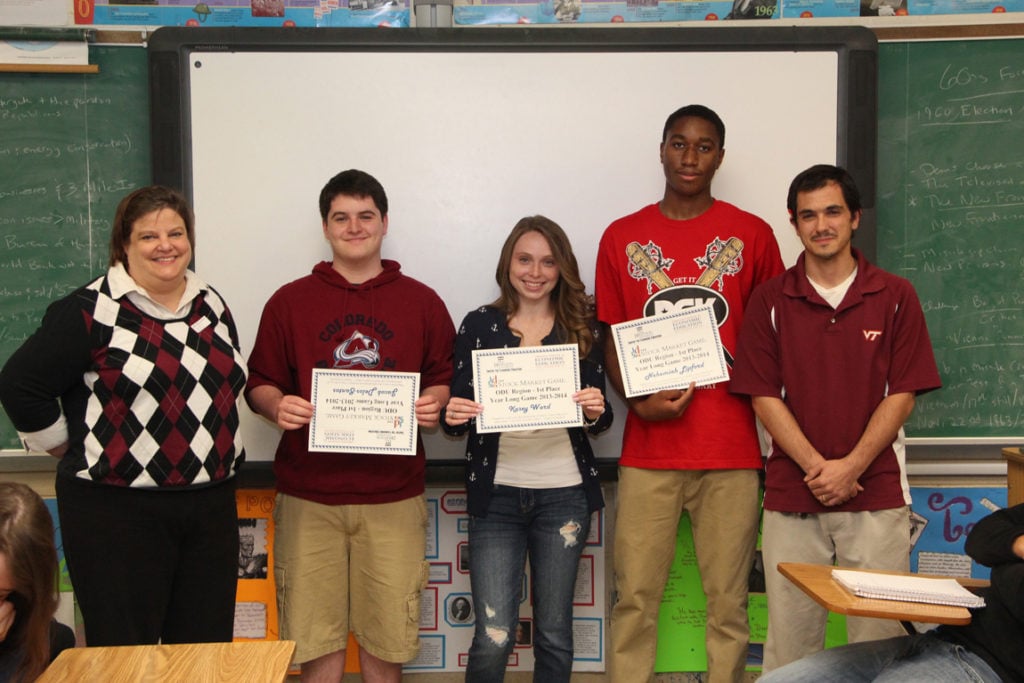

Stock Market Game News Article announcing Winners:
http://www.hampton.k12.va.us/news/bhsstock.html#.VO9GA0bqmu4







