Lesson Plans World History II SOL 8b: Revolutions of 1848
Standard WH II:The student will demonstrate knowledge of political and philosophical developments in Europe during the nineteenth century by
Objectives
b) describing unsuccessful revolutions on the continent and political reform in the United Kingdom
Lesson Plans
Introduction: A Bell-ringer activity
Notes: Students copy-down and discuss teacher generated notes
Activities: Students complete various in class activities to support learning including video analysis, maps, charts, diagrams, graphic organizers, worksheets, text-book questions, group discussion, KWL Charts etc.
Assessment: Informal, Formal, Exit-Questions, Teacher Questioning. Quizzes, Tests, Projects
Essential Knowledge:
-National pride, economic competition, and democratic ideals stimulated the growth of nationalism.
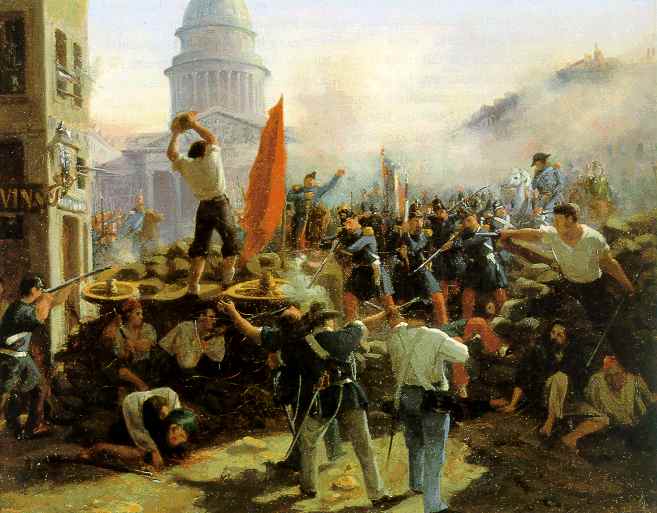
-The terms of the Congress of Vienna led to widespread discontent in Europe, especially in Italy and the German
states. Unsuccessful revolutions of 1848 increased nationalistic tensions.
-In contrast to continental Europe, the United Kingdom expanded political rights through legislative means and
made slavery illegal in the British Empire.
Activities That Support Lesson Plans
Premium Lesson Plans: 1848 Revolutions and UK Reform Short and Long activities: Includes two different activities. A long chart analysis in which students examine the causes of nine different revolutions and a short except activity where students compare six different revolutions. Students then answer four questions. Includes teacher answers. If using the long activity you may wish to divide students up and allow students to present their answers to the class OR make it a learning station-style activity where students rotate to different stations.
Les Miserables Reading : brief excerpt from the book Les Miserables
Back to World History II Virginia SOL Page