Lesson Plans World History II SOL 4e and 4f: Atlantic Slave Trade
Standard WH II:
The student will demonstrate knowledge of the impact of the European Age of Discovery and expansion into the Americas, Africa, and Asia by
Objectives:
e) mapping and explaining the triangular trade;
f) describing the impact of precious metal exports from the Americas.
Lesson Plans
Introduction: A Bell-ringer activity
Notes: Students copy-down and discuss teacher generated notes
Activities: Students complete various in class activities to support learning including video analysis, maps, charts, diagrams, graphic organizers, worksheets, text-book questions, group discussion, KWL Charts etc.
Assessment: Informal, Formal, Exit-Questions, Teacher Questioning. Quizzes, Tests, Projects
Essential Knowledge:
SOL 4e and 4f
The triangular trade linked Europe,
Africa, and the Americas. Slaves, sugar,
and rum were traded.
Export of precious metals
• Gold and silver exported to Europe
and Asia
• Impact on indigenous empires of the
Americas
• Impact on Spain and Intentional trade
Activities That Support Lesson Plans
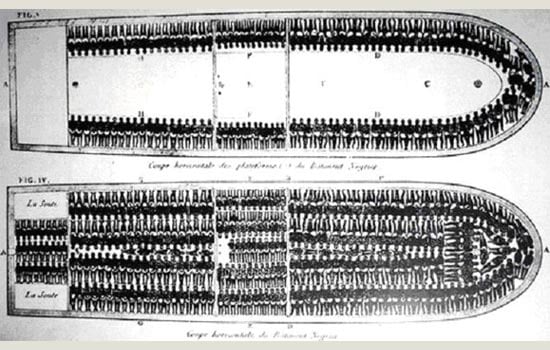
Joseph Cinque Amistad takeover ship on Middle Passage
Tobacco Economy and Slave Life Analysis Tobacco Economy and Slave Life Analysis for use also with Tobacco Economy video hosted at the Jamestown-Yorktown Foundation: http://www.historyisfun.org/video/tobacco-economy/
Note: With the above Tobacco Economy activities I only use the document analysis portion comparing slave life with that of the slave-master.e
Tobacco Economy Jamestown Video Guide: Show the video here and have students complete the lesson on the video.
12 Years a Slave Video Lesson Plans and Worksheet: Might be used for an end of the year/unit activity. May also be good to show a clip of it in class and discuss it.
Crash Course World History: Atlantic Slave Trade. Students write down any 5 facts.
Note: The above activities are best used with the Virginia Prentice Hall World History: The Modern Era textbook.
Back to World History II Virginia SOL Page
[counterize type=”hits” version=”no”]



